Spine Health and Scoliosis
- Health
- Spine Health and Scoliosis
These types of diseases, also called spinal deformities, require a complete understanding of the deformity through various imaging and measurement methods in order to be treated correctly. Scoliosis, or curvature of the spine, accounts for approximately 80% of structural deformities. Depending on the degree of curvature, scoliosis may go unnoticed for many years, or it may put pressure on the lungs, requiring urgent intervention. If the disease is detected late, it can lead to various health problems, especially growth and developmental delays in childhood. Therefore, having sufficient knowledge about scoliosis and being able to recognize its signs and symptoms early is extremely important for the course of the disease
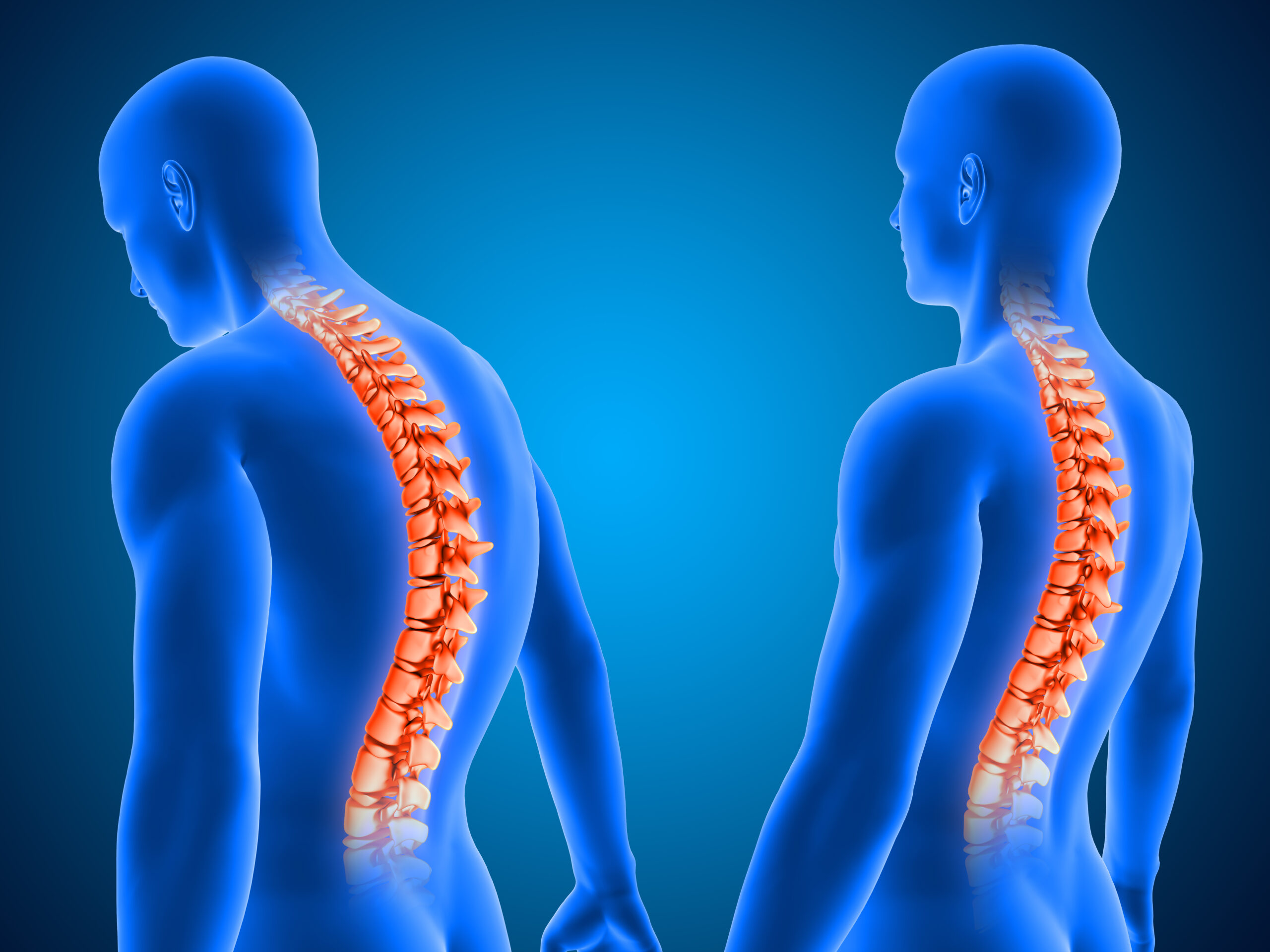
What is scoliosis (spinal curvature)?
Scoliosis is the most common spinal deformity and is a three-dimensional spinal deformity that causes extremely serious postural abnormalities in advanced stages. This deformity can arise from structural defects in the spine or develop due to non-spine causes. Non-structural scoliosis usually partially corrects itself over time or becomes undetectable when the underlying cause is eliminated. Structural scoliosis, on the other hand, often occurs idiopathically, but neuromuscular diseases, connective tissue disorders, infectious or neoplastic conditions, neurofibromatosis, degenerative and rheumatic diseases, metabolic disorders, and various traumatic effects can also lead to structural curvature of the spine.
Is idiopathic scoliosis congenital?
Scoliosis cases where the structural curvature of the spine is unknown are called idiopathic scoliosis, and approximately 80% of all scoliosis cases fall into this category. This complex spinal pathology, thought to arise due to multiple factors during the rapid growth period of childhood, is usually painless and asymptomatic. Therefore, it is quite difficult to detect. In cases that progress without early diagnosis and are left untreated, acute or chronic back and lower back pain occurs, heart and lung functions are impaired, and physical mobility is restricted. The risk of depression increases due to the cosmetic defect, and the person’s quality of life is significantly impaired. The risk of sudden death is high in severe curvatures.
What causes scoliosis?
Idiopathic scoliosis, which affects 2 to 4 out of every 100 healthy children, has an unknown cause. However, some factors associated with its occurrence can be listed as follows:
- The functioning of structural elements in the spine.
- How neuromuscular structures function
- The presence of certain diseases such as posterior colon dysfunction
- Hormonal elements
- Biomechanical factors
- Birth characteristics such as gender, developmental traits, and genetic predisposition
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Unhealthy eating habits
- Socioeconomic status
- Working in jobs that require asymmetrical loading on the spine.
What are the symptoms of scoliosis?
Scoliosis begins insidiously and can progress without any symptoms for a long period. Pain is usually absent, and the vast majority of cases are discovered incidentally on radiographs taken for other reasons. However, in individuals with loss of flexibility in the hamstring muscles, decreased spinal flexion capacity, and weakness in the abdominal and back muscles, severe lower back pain may occur as a result of certain physical activities. Furthermore, considering the relationship between the spine and the rib cage, individuals with severe curvature experience shallow breathing and frequent respiratory infections due to decreased chest compliance. It should be noted that progressive and untreated cases increase susceptibility to depressive mood and various mental illnesses, and that spinal curvatures greater than 90° are associated with sudden infant death syndrome.
How is scoliosis treated?
Early diagnosis is the first step in the treatment of idiopathic scoliosis. Early diagnosis, especially during adolescence, aims to prevent the progression of the curvature, to reverse the spine to the optimal angle if possible, and thus to improve both aesthetics and posture. The goal of advanced scoliosis treatments is primarily to alleviate pain in the spine, improve accompanying physical problems, and correct respiratory dysfunction.
Get Expert Advice
Connect with our experts to learn about the process, get your questions answered, and receive step-by-step guidance designed for your needs.
